dBSea Software
Underwater Noise Prediction
dBSea – Underwater noise prediction and visualisation software
dBSea has been developed by Marshall Day Acoustics and Irwin Carr Consulting as a powerful tool for the prediction of underwater noise in a variety of environments.
dBSea is ideal for the investigation of underwater acoustic problems involving single or multiple sources using solvers covering a wide frequency range.
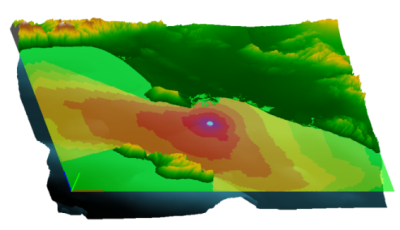
The software incorporates a user friendly interface and clearly defined workflow that allow models to be quickly developed and modified. The 3D workspace allows clear visualization of bathymetry data, noise sources and prediction results. Marshall Day release a 64bit dBSea version to allow the modeling of larger area.
The software allows the prediction in 1/1 or 1/3 octave bands and using two solvers for a lower and upper frequency range. The maximum frequency range is 12.5 Hz to 160 kHz (1/3 Octaves) and 16 Hz to 128 kHz (1/1 Octaves).
Please contact Navcon to receive a dBSea link and Trial License
Technical Information
The solvers incorporated into dBSea to predict the underwater sound field comprise the most popular calculation methods used in the underwater acoustics industry.
The different solver algorithms each find application with different types of problems, adding up to an overall package that covers many underwater acoustics scenarios, and considers complex sound speed profiles and sediment properties. dBSea incorporates source directivity for airgun seismic survey predictions and plots output levels as SPL, SEL, SPL peak or SPL peak to peak.
These solvers make dBSea a robust and reliable tool for consultants and other technical professionals.
dBSeaPE – parabolic equation method
The dBSeaPE solver makes use of the parabolic equation method, a versatile and robust method of marching the sound field out in range from the sound source. This method is one of the most widely used in the underwater acoustics community, and offers excellent performance in terms of speed and accuracy in a range of challenging scenarios.
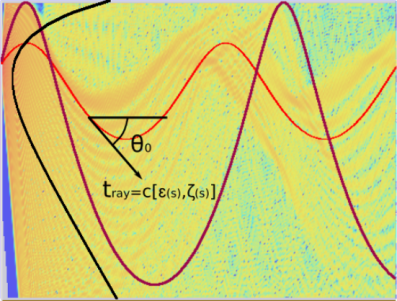
dBSeaRay – ray tracing method
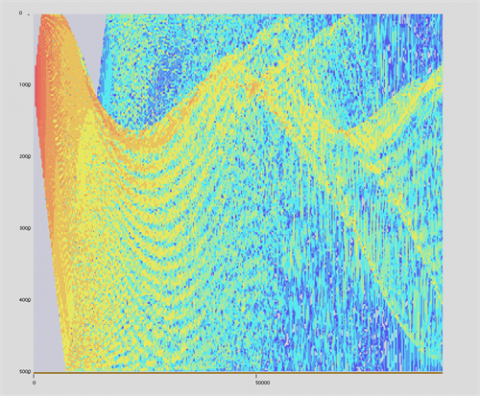
The dBSeaRay solver forms a solution by tracing rays from the source to the receiver. A large number of rays leave the source covering a range of angles, and the sound level at each point in the receiving field is calculated by coherently summing the components from each ray.
dBSeaModes – normal modes method
The normal modes are calculated for each water depth, based on the sediment properties and water sound speed profile. The sound field is calculated by assuming that energy only travels outward from the source, and that energy is not passed between modes (adiabatic assumption), leading to coupled mode equations.
User defined equation
The user can use two rapid solvers (20 log and 10 log) and a user defined equation for quick evaluation of problems.